What Is Government Intervention?
Sometimes the government feels the free market is not achieving the optimal result they want and so they intervene with various methods to set it back on track.
The different types of government intervention are:
- Indirect tax
- Subsidies
- Price ceilings
- Price floors
Indirect Tax
What is it?
This is when the government says that for every unit of a good the consumer must pay a higher price. The difference in price is the tax and this is given to the government. The tax will cause the supply curve to shift up and hence the price equilibrium will shift to a higher value.
Why is indirect tax set?
- Gains government revenue
- Decreases consumption of demerit goods like cigarettes
- Redistributes income in a population. (Robin hood taking from the rich giving to the poor)
- To correct negative externalities and socially inefficient allocation of resources
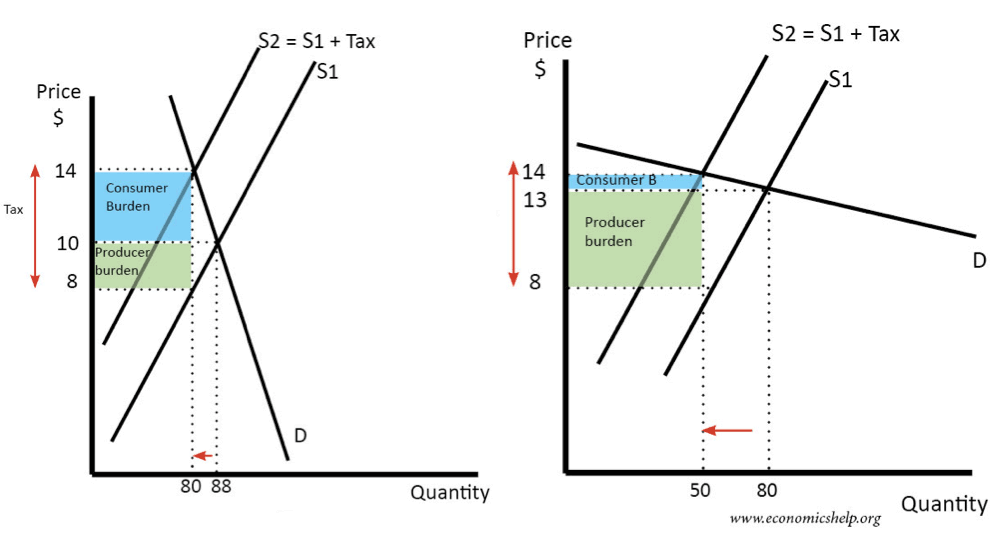
Tax incidence (HL)
When a tax is imposed it is able to negatively affect both the consumer and the producer but it is not always equal.
The tax itself can be calculated by multiplying the units demanded by the tax. (p1-pe)*Qe
From this tax we are able to look at what price was payed by the producer and what by the consumer by drawing a line from the old equilibrium and cutting through the tax area. This divides it into two sections that which is above the equilibrium and that below.
What determines the size of the area is the difference in elasticity of demand and supply. If you want to remember which will and can cause which just draw a quick sketch and look at the area sizes.
Consumers bear most burden: Demand is less elastic than supply. This is because if it's inelastic consumers don't care about price changes so producers just pass all the burden to them.
Producers bear most burden: Demand is more elastic than supply. This is because producers don't want to lose all demand to annoyed costumers so they take the burden.
Subsidies
Definition: This an amount of money granted by the government towards producers. It is often given per unit of output and causes the producers to be able to produce more a ta lower price.

A subsidy causes the supply curve to shift down by the subsidy.
Why are subsidies given?
- To increases the revenue of the hardworking, but low payed producers in their country
- To increase consumption of a good considered positive to society.
- To make the basic necessity goods more affordable to low-income consumers
- To promote growth of an industry.
- To correct positive externalities, in order to fix the market.
- To encourage exports of the product to foreign countries.
Price Floor
Definition: This is when the government sets a minimum price on a product which all producers must legally set their price above.
This is done to protect producers as it forces the price of the product to go up. Now hardworking producers, who normally receive very little, can now get a more ethical price. This encourages more producers to produce this product because they know they'll be payed more for it.
What problems does this cause?
The higher price causes demand to decrease and supply to increase. This creates an excess of supply - a surplus.
The surplus is bad because it means a lot of product is being made but the companies are unable to sell it. They are losing money even with the higher price and they were forced by law to do this.
- Surplus
- Potential black markets selling at regular prices.

How to fix the surplus
In order to fix the surplus the government must either increase demand or decrease supply. Here are some ways they can do that.
Increase demand
- Government buys and stores the excess supply
- Government sells the good internationally, but would need to subsidize it in order for it to be able to compete on internal markets
- Government buys the good and gives it away as foreign aid.
- Government can burn the excess supply. This is quite unethical.
Decrease supply
- Pay the suppliers to not produce the good and produce something else.
Price Ceiling
Definition: This is when the government sets a maximum price on a product which producers are not allowed to set their price above.
This is done to protect consumers as it means products which might normally be expensive are now much cheaper. Now the consumer can afford products which they really wanted but were outside their price range.
What problems does this cause
It is the opposite problem to what happened with a price floor. Now their is high demand, as consumers are jumping at the low prices, but low supply as most producers can't afford to supply there product at the minimum price. Therefore there is an excess of demand or a shortage

How to fix the shortage
In order to fix the shortage the government must either increase demand or decrease supply. Here are some ways they can do that.
Increase supply
- Government grants subsidies to producers to encourage them to produce more of the good
- Before setting the price ceiling the government buy a lot of the good and keep it in storage. Then after imposing the ceiling, during the shortage they could release stock to meet demand.
- Government produces the good itself in order to meet the demand.
Editors- joeClinton - 884 words.
- DanyalWantensICS - 972 words.
- RuY2718 - 3 words.
View count: 22118